In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cyber threats are becoming more prevalent and harmful. Protecting yourself and your information from these threats is known as cybersecurity. This involves safeguarding our systems, networks, and data to keep them safe from unauthorized access, changes, or destruction.
When people think of cybersecurity, they often picture a hacker in a dark room, surrounded by glowing computer screens filled with code, wearing a hoodie as they launch cyberattacks. If you’ve seen Mr. Robot, you know what I’m talking about. While this makes for great movie scenes, cybersecurity is much more that hacking and coding. It also involves protecting our personal and business information from threats that come from human actions, also known as social engineering, where attackers manipulate and trick people into giving away sensitive information—a method which many of us know have encountered via phishing emails, scam calls, or fraudulent websites. Understanding these risks is key to keeping our digital lives secure.
Table of Contents
- What is Cybersecurity?
- Cybersecurity Best Practices: Essential Steps to Stay Safe
- Why Cybersecurity Matters More Than Ever
- Getting Started in Cybersecurity
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting digital systems, networks, and sensitive information from cyber threats such as malware, ransomware, phishing, and hacking attempts. It involves a combination of technologies, processes, and best practices designed to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and disruptions. As cyber threats continue to evolve, cybersecurity remains a critical field that helps individuals, businesses, and governments defend against potential attacks and maintain a secure digital environment.
Why Cybersecurity Matters
In 2025, cybersecurity is more important than ever. As technology becomes more advanced, so do the threats we face. Businesses need strong cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data from being stolen. After all, cybersecurity is not just a technical necessity—it’s a fundamental aspect of protecting our digital lives in an era where data is one of the most valuable assets. Without these protections, companies might suffer financial losses or damage to their reputation.
With the increasing reliance on digital systems, the demand for cybersecurity jobs is also on the rise. Skilled professionals are needed to tackle new and evolving attacks. These experts use their knowledge to defend against hackers, spammers, and other cybercriminals. It’s not just about having the right tools but also having the right people who understand these threats.
The role of cybersecurity is not limited to just businesses. It extends to governments and individuals as well. As attacks become more sophisticated, there’s a growing need for comprehensive solutions that can protect everyone. Whether it’s securing personal information or safeguarding enterprise data, I see cybersecurity as essential in protecting our digitally connected lives.
Cybersecurity Pillars: People, Processes, and Technology
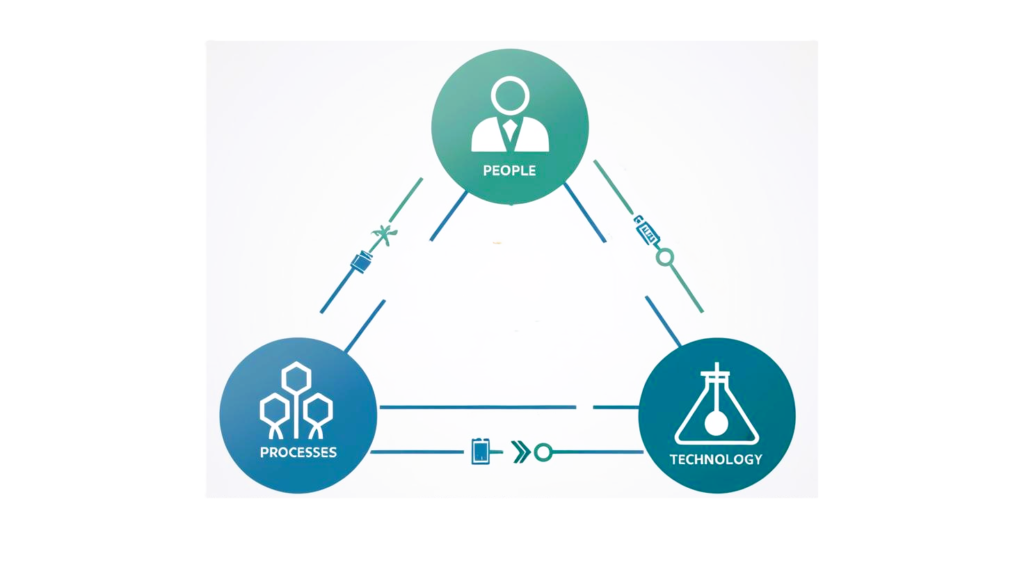
A cybersecurity framework diagram illustrating the relationship between People, Processes, and Technology, emphasizing the balance needed for effective security.
Cybersecurity isn’t just about installing antivirus software or using strong passwords. It revolves around three key elements; people, processes, and technology. In order for any business to operate effectively, there needs to be a balance between these three; one cannot function without the other.
1. People
Every person, from average users to IT experts, has a critical part to play in maintaining security. People are essential in recognizing threats such as phishing and other social engineering tactics. These threats specifically target individuals by persuading them to reveal private information.
To minimize the risk, it is important to have cybersecurity awareness training. This training helps decrease human error, which is a major vulnerability in security systems (also known as insider threat). Remember, even the most secure settings can be jeopardized by a simple human mistake.
2. Processes
Employing effective processes and procedures is crucial in maintaining a secure environment. Organizations should implement security strategies and guidelines to protect their information. These include Incident Response (IR) plans that define roles, responsibilities, methods of communication, and provide guidelines for addressing cyber threats quickly and effectively.
Following recognized cybersecurity standards like NIST 800-53, ISO 27001, and CIS Controls strengthens a company’s defenses and minimizes risks to both security and business operations. Processes ensure that everyone follows the same rules, which ultimately helps keep data safe.
Here’s a simple list of key practices:
- Establish clear security policies
- Use regular audits and assessments
- Implement Incident Response strategies
- Adhere to established cybersecurity frameworks
3. Technology
Having the right technological tools is essential for safeguarding sensitive information. Technologies such as encryption, firewalls, and multi-factor authentication play a big role in protecting data.
Security tools also include VPNs and antivirus software, which help ensure online safety. Moreover, cloud security measures prevent hackers from accessing stored online data, maintaining the safety of your information. Using these tools can support the procedures and actions necessary to build a secure environment.
Security Tools:
| Technology | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Firewalls | Block unauthorized access |
| Encryption | Protects data by scrambling contents |
| Multi-factor authentication | Adds an additional layer of security |
| VPNs | Securely connects remote devices over the internet |
| Antivirus software | Detects and removes malicious software |
| Cloud security | Protects data stored in the cloud |
In short, understanding and implementing these three pillars—people, processes, and technology—ensures a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. Each element supports the other, creating a robust barrier against potential cyber threats.
Common Cybersecurity Threats

Understanding cyber threats is the first step to staying protected. Here are the most common ones:
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing remains one of the most effective ways hackers steal sensitive information. These scams often come in the form of emails, text messages, or fake websites designed to trick you into revealing personal details like passwords or credit card numbers.
How It Works:
- You receive an email that appears to be from a trusted source (your bank, employer, or a service like PayPal).
- The email contains a malicious link leading to a fake website that looks legitimate.
- Once you enter your credentials, they are send to the attacker.
- Attacker then uses your credentials to steal personal information.
2. Malware & Ransomware
Malware is malicious software designed to infiltrate and damage your system. Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts your files and demands payment to restore access.
How It Works:
- Malware can be hidden in email attachments, software downloads, or malicious ads—disguising itself as something harmless, much like the infamous Trojan Horse from Greek mythology.
- Just as the Greeks used a deceptive gift to infiltrate Troy, cybercriminals use malware to sneak into systems undetected.
- Once installed, it can steal sensitive data, track keystrokes, or lock you out of your own files.
3. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
A MitM attack occurs when a hacker intercepts communication between two parties, such as when you connect to an unsecured public Wi-Fi network (i.e. free airport or coffee shop Wi-Fi).
How It Works:
- A hacker creates a public Wi-Fi and names it similar to the establishment.
- You connect to the unsecured Wi-Fi network at a café or airport. For example, at a Starbucks, a hacker might name the Wi-Fi “Starbucks_Free_Wi-Fi_2.4Gz”
- When someone connects to an unsecured Wi-Fi, the hacker intercepts the connection, allowing them to monitor your activity and steal sensitive data like passwords or financial information.
4. Credential Stuffing & Password Attacks
Cybercriminals use leaked or stolen usernames and passwords, typically attained from a breach or phishing attack, to gain unauthorized access to online accounts.
How It Works:
- Hackers use automated tools to try large databases of stolen credentials.
- If you reuse passwords across multiple accounts, they can easily break in.
5. Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering relies on psychological manipulation to trick victims into revealing confidential information. These attacks may involve impersonation, urgency tactics, or emotional appeals.
How It Works:
- You receive a phone call from someone claiming to be tech support, warning of a security issue.
- They instruct you to install software (actually malware) or provide login details.
Cybersecurity Best Practices: Essential Steps to Stay Safe
1. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
- Avoid using common passwords like “123456” or “password.”
- Use a mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols. Essentially, a complex password.
- Consider using a password manager like NordPass to generate and store secure passwords.

2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification step (e.g., a one-time code sent to your phone or a hardware token).
- Consider using an authentication app or a hardware security key like YubiKey for enhanced protection.
3. Stay Alert for Phishing Attacks
- Always consider the context of unexpected messages—if you weren’t expecting an email or text, be cautious before clicking links or opening attachments.
- Don’t let curiosity get the best of you; verify the sender before responding to urgent requests.
4. Update Your Software Regularly
- Regularly update your operating system, browsers, and applications to patch vulnerabilities.
- Install and maintain reputable antivirus software and firewall protection.
5. Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Sensitive Transactions
- Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) like NordVPN to encrypt your connection when browsing on public networks.
- Never access financial accounts or enter passwords over public Wi-Fi.

6. Monitor Your Online Accounts
- Regularly check bank statements and credit reports for suspicious activity.
- Set up security alerts for unauthorized login attempts.
7. Back Up Important Data Regularly
- Use cloud storage or an external hard drive to back up essential files, such as Western Digital’s My Cloud Home Network Attacked Storage
- My experience with personal cloud storage has been excellent. It ensures you have controlled storage of your photos, videos, and files into a centralized device.
- Ensure backups are encrypted and stored securely to prevent data loss from ransomware attacks.
8. Educate Yourself & Stay Informed
- Cyber threats constantly evolve—stay up to date on the latest scams and security best practices.
- Follow cybersecurity experts and organizations for updates on emerging threats.
By following these best practices and leveraging the right cybersecurity tools, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to cyberattacks. Cybersecurity is a shared responsibility—stay vigilant and proactive in protecting your digital presence.
Why Cybersecurity Matters More Than Ever
Cybersecurity is not just an IT concern—it affects everyone. Whether you’re an individual, a business owner, or an IT professional, protecting your digital assets is crucial. With rising cyber threats, taking proactive security measures can prevent identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage.
Getting Started in Cybersecurity
If the importance of cybersecurity has sparked your interest, you’re not alone. Cybersecurity is a growing field and Cybersecurity professionals are in high demand, with job opportunities expected to grow by 33% through 2030—much faster than most occupations.
Whether you’re looking to change careers or enhance your current role with security knowledge, training and certification are often the best first step. Professional certifications validate your skills and demonstrate commitment to potential employers.
For newcomers to the field, starting with beginner-friendly certifications can provide a solid foundation. These programs teach essential concepts while preparing you for more advanced specializations later.
Want to take the first step in your cybersecurity journey? Check out our comprehensive guide to the Best Cybersecurity Certifications for Beginners In 2025. This resource breaks down the most valuable entry-level certifications, comparing costs, difficulty levels, and career impact to help you make an informed decision about your professional development path.




